Deploying MySQL on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure – MySQL Database Service
With Oracle’s recent release of MySQL Heatwave, I’ve been looking more into MySQL. I’ve actually...
With the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) MySQL Database Services, in order to connect you have to access MySQL through a compute node. This means you will have to create a compute node within OCI. You can do this quickly with Terraform (here).
Once you have an OCI compute node built, you will need to install MySQL Shell. MySQL Shell is the advanced MySQL Client for Developers and DBAs. Making interaction with MySQL easier from the command line.
Access the OCI compute node (needs public IP address of compute node)
> ssh -I .ssh/mysql_private_key.pem opc@<public IP address>
Install MySQL Shell via command line
> sudo yum install -y mysql-shell
After MySQL Shell is installed, you can access your MySQL Database Service (database) via the command line.
To start MySQL Shell and connect to the DB System endpoint, the following command is used. Keep in mind, you are SSHed into the compute node, from the compute node you’ll use the DB System private IP address to connect.
> mysqlsh bcurtis@10.0.0.37
Provide the password for the user that was established when creating the MySQL Database Service.
After providing the password, you will be connected to the MySQL Database Service. By default the MySQL Shell will connect you to the JavaScript command line option. I’ve switched to the SQL command line option by using “\sql”.
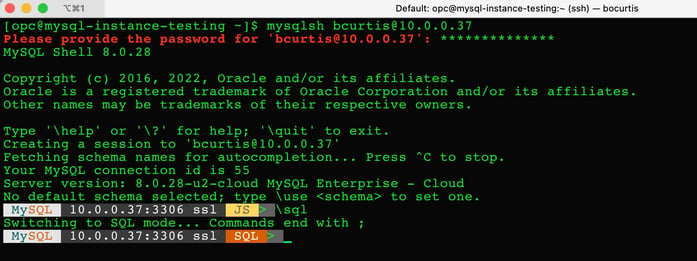
At this point, you can now interact with your MySQL database on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
With Oracle’s recent release of MySQL Heatwave, I’ve been looking more into MySQL. I’ve actually...
When building MySQL Heatwave Systems (use to be called MySQL Database Service or MDS), the need to...
MySQL has long been the number two database in the world! Initially MySQL started as one of the...